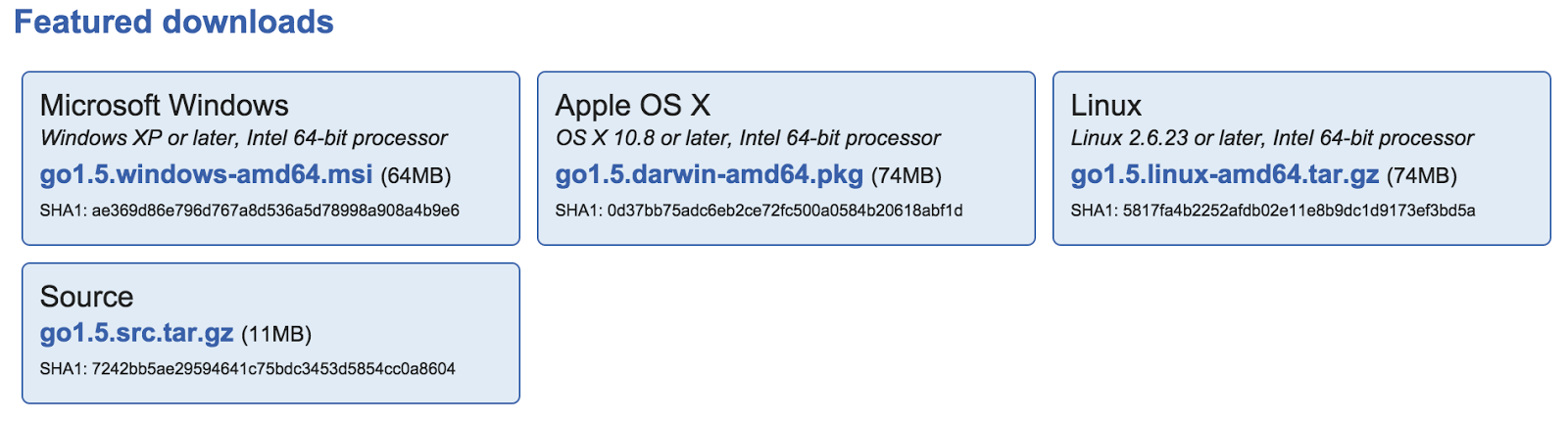
Version 9.2 of GDB, the GNU Debugger, is now available for download. See the ANNOUNCEMENT for details including changes in this release. An errata list and documentation are also available. News September 13th, 2020: GDB 10 branch created. The GDB 10 branch (gdb-10-branch) has been created. To check out a copy of the branch use. How to install gdb on OSX 10.9? I try to use macports: port install gdb Password. Updating database of binaries: 100.0% - Scanning binaries for linking errors: 100.0% - No broken files found. But I don't have gdb executable: $ which gdb $ I found out that macports gdb on mac is called ggdb. This videos explains the step by step process to insall gdb debugger and gcc in windows 10. First of all you need to go to download page of minGW by clicking.
Estimated reading time: 6 minutes
Docker Desktop for Mac is the Community version of Docker for Mac.You can download Docker Desktop for Mac from Docker Hub.
By downloading Docker Desktop, you agree to the terms of the Docker Software End User License Agreement and the Docker Data Processing Agreement.
What to know before you install
Relationship to Docker Machine: Installing Docker Desktop on Mac does not affect machines you created with Docker Machine. You have the option to copy containers and images from your local default machine (if one exists) to the Docker Desktop HyperKit VM. Whenyou are running Docker Desktop, you do not need Docker Machine nodes running locally (or anywhere else). With Docker Desktop, you have a new, nativevirtualization system running (HyperKit) which takes the place of theVirtualBox system.
System requirements
Your Mac must meet the following requirements to successfully install Docker Desktop:
Mac hardware must be a 2010 or a newer model, with Intel’s hardware support for memory management unit (MMU) virtualization, including Extended Page Tables (EPT) and Unrestricted Mode. You can check to see if your machine has this support by running the following command in a terminal:
sysctl kern.hv_supportIf your Mac supports the Hypervisor framework, the command prints
kern.hv_support: 1.macOS must be version 10.14 or newer. That is, Mojave or Catalina. We recommend upgrading to the latest version of macOS.
If you experience any issues after upgrading your macOS to version 10.15, you must install the latest version of Docker Desktop to be compatible with this version of macOS.
Note: Docker supports Docker Desktop on the most recent versions of macOS. Docker Desktop currently supports macOS Mojave and macOS Catalina.
As new major versions of macOS are made generally available, Docker stops supporting the oldest version and support the newest version of macOS.
At least 4 GB of RAM.
VirtualBox prior to version 4.3.30 must not be installed as it is not compatible with Docker Desktop.
What’s included in the installer
The Docker Desktop installation includes Docker Engine, Docker CLI client, Docker Compose, Notary, Kubernetes, and Credential Helper.
Install and run Docker Desktop on Mac
Double-click
Docker.dmgto open the installer, then drag the Docker icon to the Applications folder.Double-click
Docker.appin the Applications folder to start Docker. (In the example below, the Applications folder is in “grid” view mode.)The Docker menu in the top status bar indicates that Docker Desktop is running, and accessible from a terminal.
If you’ve just installed the app, Docker Desktop launches the onboarding tutorial. The tutorial includes a simple exercise to build an example Docker image, run it as a container, push and save the image to Docker Hub.
Click the Docker menu () to seePreferences and other options.
Select About Docker to verify that you have the latest version.
Congratulations! You are now successfully running Docker Desktop.
If you would like to rerun the tutorial, go to the Docker Desktop menu and select Learn.
Uninstall Docker Desktop

Osx Gdb
To unistall Docker Desktop from your Mac:
- From the Docker menu, select Troubleshoot and then select Uninstall.
- Click Uninstall to confirm your selection.
Note: Uninstalling Docker Desktop will destroy Docker containers and images local to the machine and remove the files generated by the application.
Switch between Stable and Edge versions
Docker Desktop allows you to switch between Stable and Edge releases. However, you can only have one version of Docker Desktop installed at a time. Switching between Stable and Edge versions can destabilize your development environment, particularly in cases where you switch from a newer (Edge) channel to an older (Stable) channel.
For example, containers created with a newer Edge version of Docker Desktop maynot work after you switch back to Stable because they may have been createdusing Edge features that aren’t in Stable yet. Keep this in mind asyou create and work with Edge containers, perhaps in the spirit of a playgroundspace where you are prepared to troubleshoot or start over.
Experimental features are turned on by default on Edge releases. However, when you switch from a Stable to an Edge release, you must turn on the experimental features flag to access experimental features. From the Docker Desktop menu, click Preferences > Command Line and then turn on the Enable experimental features toggle. Click Apply & Restart for the changes to take effect.
To safely switch between Edge and Stable versions, ensure you save images and export the containers you need, then uninstall the current version before installing another. For more information, see the section Save and Restore data below.
Save and restore data
You can use the following procedure to save and restore images and container data. For example, if you want to switch between Edge and Stable, or to reset your VM disk:
Use
docker save -o images.tar image1 [image2 ...]to save any images you want to keep. See save in the Docker Engine command line reference.Use
docker export -o myContainner1.tar container1to export containers you want to keep. See export in the Docker Engine command line reference.Uninstall the current version of Docker Desktop and install a different version (Stable or Edge), or reset your VM disk.
Use
docker load -i images.tarto reload previously saved images. See load in the Docker Engine.Use
docker import -i myContainer1.tarto create a filesystem image corresponding to the previously exported containers. See import in the Docker Engine.
For information on how to back up and restore data volumes, see Backup, restore, or migrate data volumes.
Where to go next
- Getting started provides an overview of Docker Desktop on Mac, basic Docker command examples, how to get help or give feedback, and links to other topics about Docker Desktop on Mac.
- Troubleshooting describes common problems, workarounds, howto run and submit diagnostics, and submit issues.
- FAQs provide answers to frequently asked questions.
- Release notes lists component updates, new features, andimprovements associated with Stable releases. For information about Edge releases, seeEdge release notes.
- Get started with Docker provides a general Docker tutorial.
GDB: The GNU Project Debugger
What is GDB?
GDB, the GNU Project debugger, allows you to see what is going on`inside' another program while it executes -- or what another programwas doing at the moment it crashed.
GDB can do four main kinds of things (plus other things in supportof these) to help you catch bugs in the act:
- Start your program, specifying anything that might affect its behavior.
- Make your program stop on specified conditions.
- Examine what has happened, when your program has stopped.
- Change things in your program, so you can experiment withcorrecting the effects of one bug and go on to learn about another.
What Languages does GDB Support?
GDB supports the following languages (in alphabetical order):- Ada
- Assembly
- C
- C++
- D
- Fortran
- Go
- Objective-C
- OpenCL
- Modula-2
- Pascal
- Rust
GDB version 10.1
Version 10.1 of GDB, the GNUDebugger, is now available for download. See the ANNOUNCEMENT for detailsincluding changes in this release.An errata list (PROBLEMS) and documentationare also available.
News
The latest version of GDB, version 10.1, is available for download.
This version of GDB includes the following changes and enhancements:
- Support for debugging new targets:
- BPF (bpf-unknown-none)
- GDBserver support for the following targets:
- ARC GNU/Linux
- RISC-V GNU/Linux
- Multi-target debugging support (experimental)
- Support for debuginfod, an HTTP server for distributing ELF/DWARF debugging information as well as source code.
- Support for debugging a 32-bit Windows program using a 64-bit Windows GDB.
- Support for building GDB with GNU Guile 3.0 and 2.2 (in addition to 2.0)
- Improved performance during startup through the use of threading during symbol table loading (an optional feature in GDB 9, now enabled by default in GDB 10).
- Various enhancements to the Python and Guile APIs
- Various TUI Mode fixes and enhancements.
- Other miscellaneous enhancements:
- Detection when attaching to a process of a mismatch between this process and the executable previously loaded into GDB.
- Support for default arguments for 'alias' commands.
- GDBserver support for the following host triplets has been removed:
- i[34567]86-*-lynxos*
- powerpc-*-lynxos*
- i[34567]86-*-nto*
- bfin-*-*linux*
- crisv32-*-linux*
- cris-*-linux*
- m32r*-*-linux*
- tilegx-*-linux*
- arm*-*-mingw32ce*
- i[34567]86-*-mingw32ce*
 See the NEWS file for a more complete and detailed list of what this release includes.
See the NEWS file for a more complete and detailed list of what this release includes.The GDB 10 branch (gdb-10-branch) has been created.To check out a copy of the branch use:
The latest version of GDB, version 9.2, is available for download.
This is a minor corrective release over GDB 9.1, fixing the followingissues:

- PR tui/25586 (Resizing the source/disassembly or command window produces corrupted display)
- PR gdb/25650 (GDB can't 'printf' a convenience variable holding an inferior address)
- PR build/25981 (Use of short i386 register names breaks compilation on recent Solaris 11.4)
- PR symtab/26003 (infinite loop loading symbols from separate debug objfile)
- PR build/26029 (GDB build failure on SPARC)
The GDB maintainers are looking for contributors interestedin reversible debugging.
Late breaking information, such as recently added features, can befound in the NEWS file in the gdb source tree. Old announcements are in thenews archive.Gdb For Mac
How To Install Gdb
Please send FSF & GNU inquiries & questions to gnu@gnu.org. There are also other ways tocontact the FSF.
This page is maintained by the GDBdevelopers.
Installing Gdb On Mac
Copyright Free Software Foundation, Inc., 51 Franklin St - FifthFloor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA.
Verbatim copying and distribution of this entire article ispermitted in any medium, provided this notice is preserved.
Gdb Install Windows
Last modified 2020-10-24.
